When purchasing an OBD GPS tracker, it’s essential to understand the difference between OBD I and OBD II systems, especially in terms of compatibility and diagnostic capabilities.
What is an OBD GPS tracker
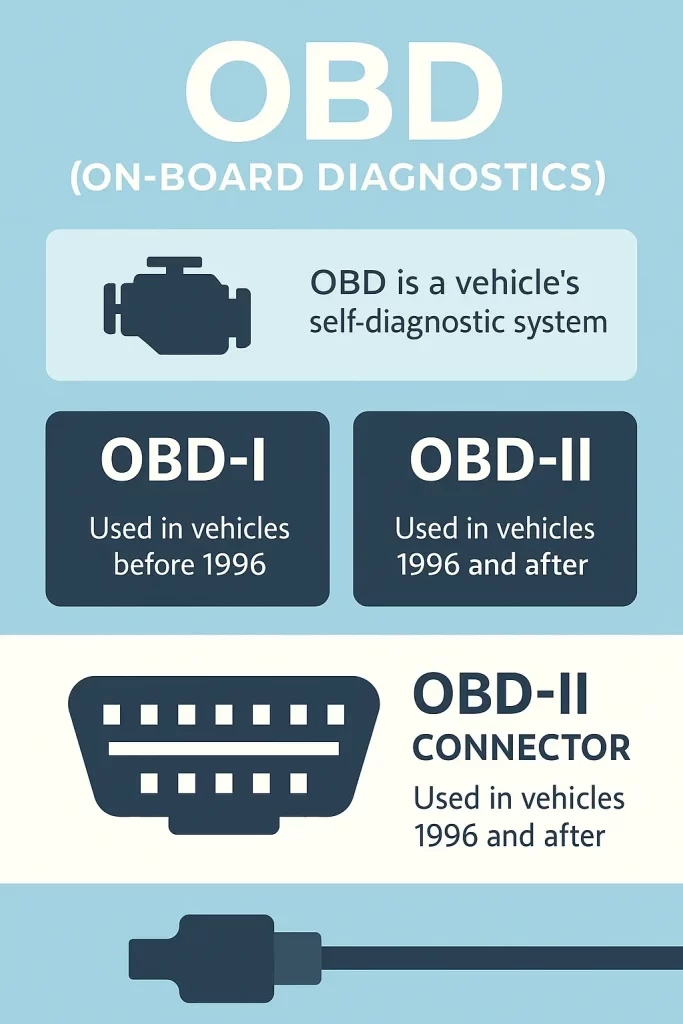
What is OBD?
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) is a vehicle system that monitors engine performance and emissions. It alerts technicians to issues and helps pinpoint faults for faster, more efficient repairs.
Over the years, OBD systems have evolved with technological advancements. Modern vehicles now feature standardized digital ports, enabling real-time diagnostics through portable devices and even mobile apps.
OBD I vs. OBD II: What Sets Them Apart?
OBD I, used in cars before the mid-1990s, focused mainly on emission monitoring. However, it lacked standardization, making diagnostics less reliable across different manufacturers.
OBD II, introduced in the early 1990s and standardized in 1996, brought significant improvements. It includes universal diagnostic codes, enhanced signal protocols, and support for remote vehicle diagnostics.
Unlike OBD I, which requires direct physical access for diagnostics, OBD II supports wireless connections (via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi), allowing data to be read remotely — a major benefit for fleet managers and vehicle owners using GPS trackers.
How to Tell If Your Vehicle Has OBD I or OBD II
Here are several ways to determine your vehicle’s OBD system:
Check the Manufacturing Year
Before 1996: Likely OBD I
1996 or later: Almost certainly OBD II
Diagnostic Port Shape
OBD II uses a 16-pin standardized connector, typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
OBD I connectors vary by make and model.
Label Under the Hood
Many vehicles have a sticker indicating OBD I or OBD II compliance.
Owner’s Manual
The manual often specifies the OBD version and compatible scan tools.
OBD GPS tracker
Can an OBD II Scanner Read an OBD I Vehicle?
In short, no — OBD II scanners and OBD I systems use different connectors and communication protocols. While adapters exist, they often provide incomplete or unreliable data due to incompatibilities. For accurate diagnostics on older vehicles, use a dedicated OBD I scanner specific to the car’s make.
Why OBD II is the Better Choice for GPS Trackers
If you’re selecting a GPS tracker for your car or fleet, OBD II is the preferred system because:
It supports remote diagnostics and data transfer
It uses standardized trouble codes
It’s compatible with most modern scan tools and tracking platforms
It enhances vehicle maintenance and fleet performance monitoring
OBD VS. OBD II Infographic
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between OBD I and OBD II helps ensure you choose the right tools for your vehicle. For most users, especially those investing in OBD GPS trackers or managing fleet diagnostics, OBD II is the clear winner due to its broader compatibility, smarter diagnostics, and remote capabilities.
FAQs sbout OBD I vs. OBD II and GPS Trackers
Generally, no. OBD2 trackers require a standardized 16-pin port only found in OBD2 vehicles. While some adapters exist, they are often unreliable for GPS tracking or diagnostics.
All cars and light trucks sold in the U.S. from 1996 onward are required to have OBD2 systems. Some models began integrating OBD2 as early as 1994–1995.
The OBD2 port is usually under the dashboard, near the steering column. In some vehicles, it might be behind a panel or close to the gear shifter or glove box.
Yes. OBD2 offers standardized trouble codes, real-time data, and compatibility with modern scan tools and GPS trackers, making it more effective than OBD1.
High-quality OBD2 GPS trackers are designed for low power consumption and won’t significantly drain your car battery. However, unplugging the device during long-term vehicle storage is recommended.
Yes. Most OBD2 GPS trackers are plug-and-play and can be installed without professional help. Just locate the port and insert the device. For more details, you can check our installation guide.
No. While both connect to the OBD2 port, scan tools read diagnostic data, whereas GPS trackers primarily monitor vehicle location, speed, and route history, though some also offer basic engine diagnostics.





